Describe the Basic Structure of an Alkane
Molecular structure of Alkanes. There are three types of alkanes.

A Level Chemistry Revision Organic Chemistry Alkanes
Alkanes are chemical compounds that consist of carbon C and hydrogen H atoms so they are also called hydrocarbons.
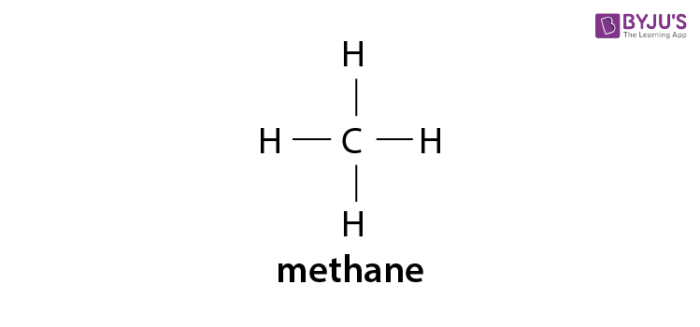
. They exhibit tetrahedral geometry with. There is no ring formation in the structure. Methane gas is the first member of the homologous series of alkanes.
Alkanes have the general chemical formula C n H 2n2. The simplest cyclic alkanes are cyclopropane C 3 H 6 a flammable gas that is also a powerful anesthetic and cyclobutane C 4 H 8 part c in Figure 372. Alkanes and Alkenes are two types of hydrocarbon families which contain carbon and hydrogen in their molecular structure.
Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin that is any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds. They can be categorized into three groups which are. C_nH_2n2 The general formula means that the number of hydrogen atoms in an alkane is double the number of carbon atoms plus two.
However it can have branched or unbranched molecular arrangements. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbon consist of carbon and hydrogen only without any functional group. C n H 2n2.
First member is Methane CH 4 Also known as Marsh gas chief constituent of natural gas 97 Hybridisation sp 3. Also called α-olefins terminal alkenes are more useful. Cyclic compound containing only carbon and hydrogen Example.
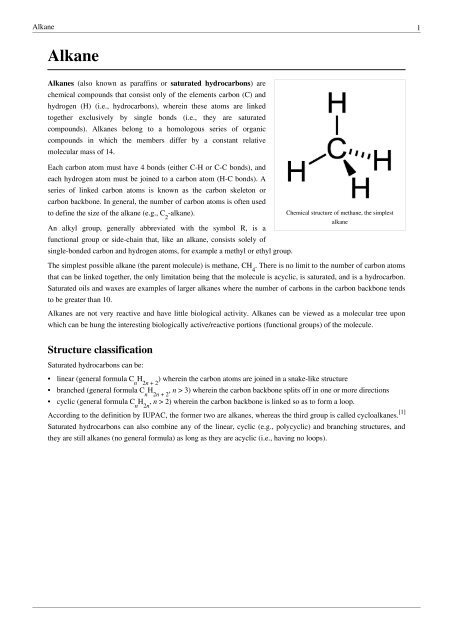
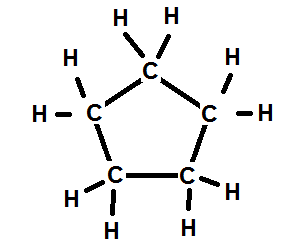
In organic chemistry an alkane or paraffin a historical trivial name that also has other meanings is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbon. In other words an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which all the carboncarbon bonds are single. The general formula of alkane is C n H 2n2.
In chemistry an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carboncarbon double bond. All the carbon atoms present in an alkane are s p 3 hybridized that is every carbon atom forms four sigma bonds with carbon or hydrogen atoms. The straight chain alkanes share the same general formula.
Copy this word sequence into your google doc. Alkynes are unsaturated carbon that shares a triple bond at the carbon site. The first three alkynes are gases and the next eight are liquids.
Describe the basic structure of an alkane. We will name unbranched alkanes as shown in Table 21 while we will name branched alkanes as alkyl-substituted unbranched alkanes. An alkane that has all its carbons connected in a row.
Describe the basic structure of a hydrocarbon and explain why these molecules are hydrophobic. In a molecule atoms that are not carbon or hydrogen are called Heteroatoms such as N O. Describe the polarity of alkane molecules.
M ethane - E thane - P ropane - B utane. The formula for alkanes is C n H 2n2. C X n H 2 n 2.
Eg M y - E ar - P hones - B lack. 21 Alkanes Alkane. The key difference between Alkanes and Alkenes is their chemical structure.
Answer Alkanes also known as paraffins or saturated hydrocarbon are chemical compounds that consist only of the element carbon c and Hydrogen H ie hydrocarbons wherein these atoms are linked together exclusively by single bonds ie they are saturated compounds. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons with the general molecular formula of CnH2n2 and alkenes are said to be an unsaturated hydrocarbon group since they contain a. The following sequence is the order of the first four alkanes from smallest to largest see if you can come up with an easy way to remember this sequence with your own group of words an example is given below.
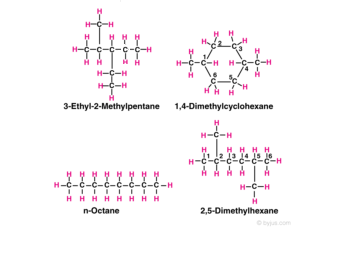
The names 3-methylhexane and 4-ethyl-3-methyloctane for the alkanes shown here are. Compound composed of only carbon and hydrogen and single bonds Acyclic Alkanes. All alkynes are odourless and colourless with the exception of ethylene which has a slight distinctive odour.
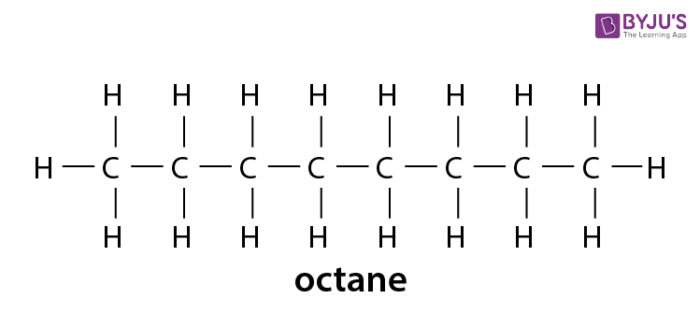
They are divided into two main classes aliphatic and aromatic. Methane CH 4 ethane C 2 H 6 propane C 3 H 8 etc. Compound composed of only carbon and hydrogen in a chain-like conformation Example.
Alkanes or saturated hydrocarbons contain only single covalent bonds between carbon atomsEach of the carbon atoms in an alkane has sp 3 hybrid orbitals and is bonded to four other atoms each of which is either carbon or hydrogen. The chemical structure of alkanes only consists of. Chain alkanes cycloalkanes and branched alkanes.
General configuration of alkane is C n H 2 n 2. Organic compounds having only two elements carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons. This gives them a general formula.
However the IUPAC recommends using the name alkene. Their structure is defined by a reactive carbon-carbon double bond they have a general formula of CnH2n they can be named by following a series of simple steps they have many uses in nature as well as in industrial and laboratory settings and some of their most common reactions include hydrogenation alkene to alkane halogenation alkene to. The most basic family of compounds has been called alkanes.
Each vertex represents a CH 2 unit. In an alkane all 4 4 4 valencies of the carbon atom are satisfied with other hydrogen atoms. The smallest alkane is Methane CH4.
Alkanes have the general molecular formula CnH2n2. Actual shape is zig-zag bc carbon is tetrahedral branched-chain alkane an alkane that has a. C X n H 2 n 2.
The properties of alkynes pretty much follow the same pattern of those of alkanes and alkenes. Alkanes are organic compounds composed of single-bonded carbon and hydrogen atoms. Alkane molecules are nonpolar.
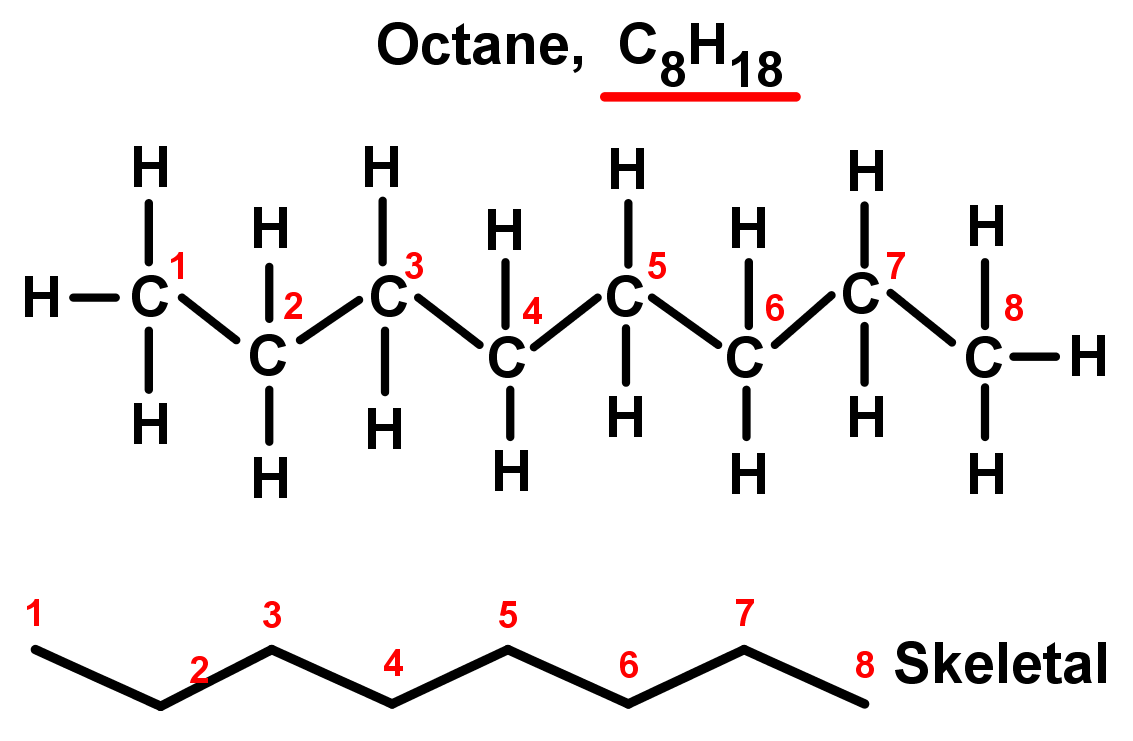
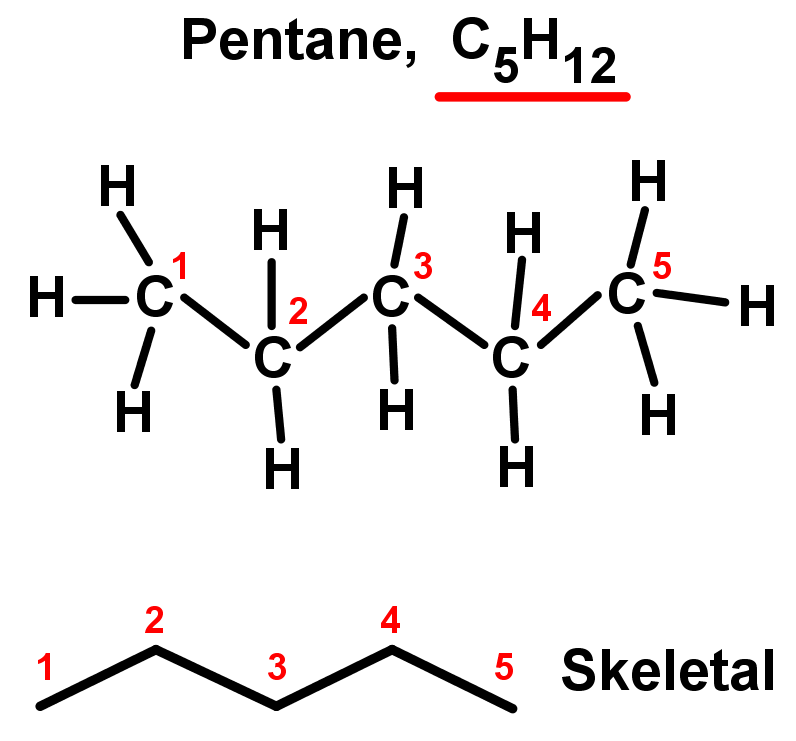
In organic chemistry alkanes such as C8H18 have structural isomers. The Lewis structures and models of methane ethane and pentane are illustrated in the figure below. The more these isomers are branched the lower the boiling point is.
They comprise only hydrogen and carbon. The alkanes are also called as paraffins. Alkane Nomenclature Rules 22A The following rules illustrate the basic principles for naming simple branched alkanes.
Up to 24 cash back ENTREE. The most common way to draw the structures of cyclic alkanes is to sketch a polygon with the same number of vertices as there are carbon atoms in the ring. The reason for this is that un-branched alkanes have a.
Unbranched Alkanes are sometimes called n-alkanes. Two general types of monoalkenes are distinguished.

Alkanes Formula List Structure Definition Examples Videos

Chemistry Pharmacy July 2010 Chemistry Basics Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Education
Alkanes Formula Definition Structure Properties List Of Alkanes Videos Examples And Faqs Of Alkanes
Ch105 Chapter 7 Alkanes And Halogenated Hydrocarbons Chemistry

Alkane Methane The Martian Chemistry Education

Basic Principles Of Organic Chemistry Chemistry Basics Medicinal Chemistry Chemistry Lessons

Lesson Explainer Properties Of Alkanes Nagwa
Alkanes Formula Definition Structure Properties List Of Alkanes Videos Examples And Faqs Of Alkanes
Alkanes Formula Definition Structure Properties List Of Alkanes Videos Examples And Faqs Of Alkanes





Comments
Post a Comment